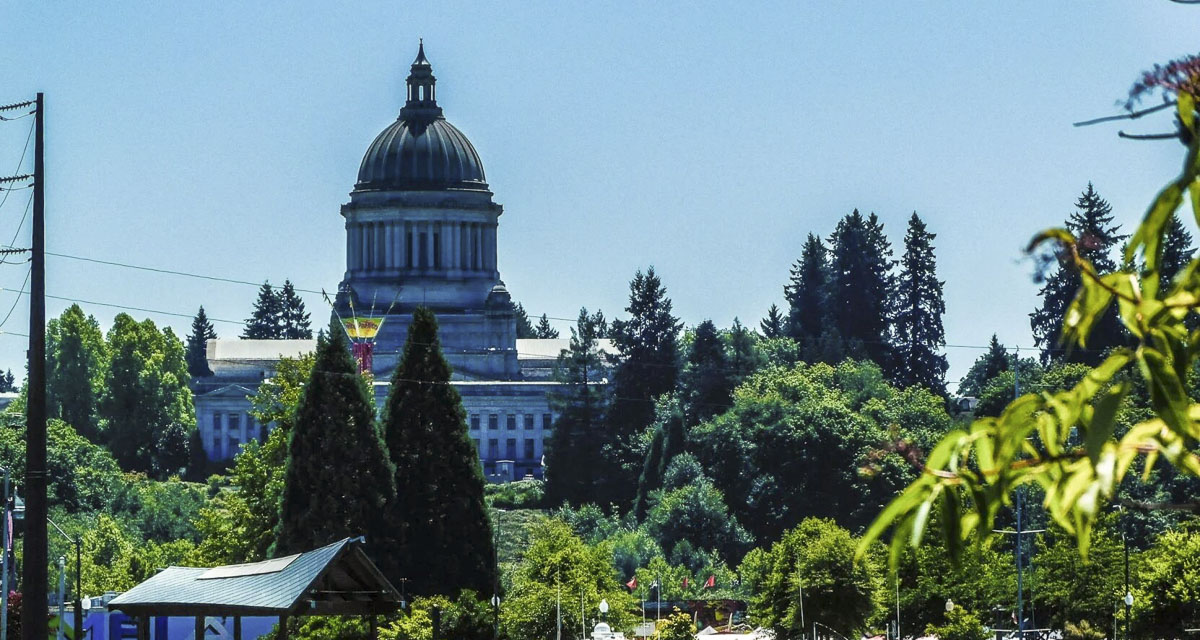
Overall spending by the state Legislature has increased 116% since the 2013-15 biennium
TJ Martinell
The Center Square Washington
Last month, the state Economic and Revenue Forecast Council reported that Washington faced running out of money by 2027. With the passage of President Trump’s One Big Beautiful Bill Act, the state now faces the loss of billions in Medicaid funding that could exacerbate Washington’s fiscal woes in the upcoming legislative sessions.
“We’re in the worst budget crisis we’ve ever had,” Gov. Bob Ferguson’s Senior Health Policy Advisor Caitlin Safford told the Senate Health & Long-Term Care Committee at its Tuesday meeting.
The One Big Beautiful Bill Act enacts changes to Medicaid eligibility, which is expected to significantly reduce the number of Washington residents on the program, known in the state as Apple Heath. While Sen. Patty Murray, D-Wash., recently claimed 250,000 would lose coverage and cause more than a dozen hospitals to close, Health Care Authority Medicaid Director Charissa Fotinos told the Health & Long-Term Care Committee she estimated 100,000 would lose coverage.
While she said that “we can’t say with any certainty how many people will lose coverage and how much money it will cost the state over the 10-year period,” she added that “the impacts will be significant.”
Safford said that “between a combination of federal rule, HR1 and the potential expiration of the enhanced advanced premium tax credits, we are going to start seeing coverage loses in January. That’s going to take an immediate hit to our uninsured rate. It’ll be a hit to providers; we’ll probably see some counties that don’t have individual market coverage, which is going be really tough. There’s going to be some tough decisions that are going have to made on the ground around how we’re structuring our health care system.”
She also said that “from the Governor’s Office, this from our perspective, this is a partnership we’re going to be having with the Legislature on how we are accomplishing everything we have to accomplish. Likely a lot of that coming in the next 60-day short session and then whatever else we need to do in a 105-days session in 2027.”
Medicaid spending in Washington state has increased fivefold since 2013, when there were 1.3 million residents enrolled. Almost a decade later and after the program was expanded by the Affordable Care Act, there were there were 2.17 million residents enrolled in Apple Health. That program now includes an expansion for illegal aliens funded solely by the Legislature operating budget at the cost of $150 million for taxpayers.
Overall spending by the state Legislature has increased 116% since the 2013-15 biennium. After facing a budget shortfall in the billions of dollars despite record revenue levels due to increased spending, the Legislature passed the largest tax increase in state history.
This report was first published by The Center Square Washington.
Also read:
- Opinion: It’s not just the increased taxes that are driving businesses awayMark Harmsworth of the Washington Policy Center argues taxes, workforce challenges and economic uncertainty are driving businesses to relocate outside Washington.
- Opinion: There is no such thing as a ‘free’ lunch, and an income tax isn’t more palatable because it offers oneElizabeth New of the Washington Policy Center argues the proposed Washington income tax and universal school meals policy reflect a broader state spending problem
- State of the City: Vancouver mayor promotes arts and culture in her annual addressVancouver Mayor Anne McEnerny-Ogle highlighted arts initiatives, public safety investments and city development projects during her annual State of the City address.
- VIDEO: WA House pulls an all-nighter as income tax debate continuesWashington House lawmakers debated Senate Bill 6346 through the night as Republicans proposed amendments and raised concerns about economic impacts and constitutional questions.
- Opinion: Democrat Party penalizes marriage in WashingtonLars Larson argues that Washington’s newly passed income tax unfairly targets married couples by creating what he describes as a financial penalty for filing jointly.