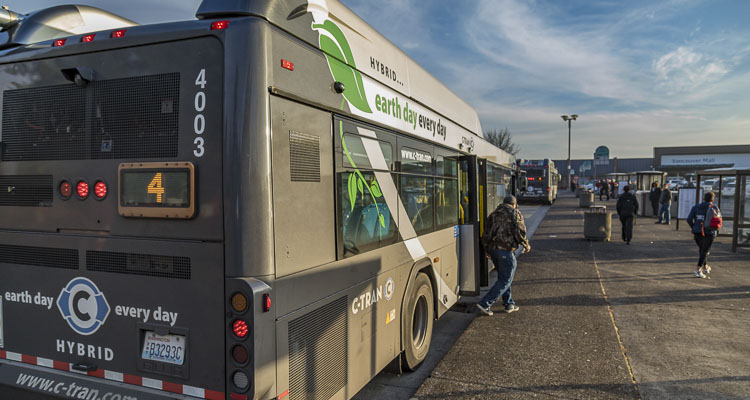
Once the pandemic hit, transit operational costs increased while passengers abandoned public transportation for various reasons
Elyse Apel, Tom Gantert and Brett Rowland
The Center Square
In 2019, transit agencies across the U.S. for all modes of transportation took in 32.3 cents in fares for every dollar they spent on operating costs.
Those transit agencies recovered 18.4 cents in fares on the dollar in 2020 and just 12.8 cents in 2021.
Once the pandemic hit, transit operational costs increased while passengers abandoned public transportation for various reasons – including fear of COVID-19, working from home and having some transportation shut down.
That loss in farebox revenue was made up by an injection of federal taxpayer dollars. The federal government gave transit agencies $71.7 billion in four relief packages in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, according to a report from rating agency S&P.
The National Transit Authority stated 852 transit agencies across the U.S. spent $13.1 billion in federal pandemic relief funds mostly on operational expenses in 2021, a 95 percent increase from the previous year.
All forms of transit saw the percentage of farebox revenue compared to operating expenses drop in 2021. For example, farebox revenue was 49.1 percent of operating expenses in 2019, the year before the pandemic hit. In 2021, the farebox revenue dropped to 19 percent.
Recently released data from the Federal Transit Administration sheds light on how the COVID-19 pandemic continued to cripple public transportation throughout 2021 and how federal taxpayer funding kept it running.
Federal funding was the predominant source of funding for transit, something the report says was due to the “COVID-19 public health emergency.”
From 2021 to 2020, federal funding for transit operating expenses rose dramatically. In 2020, federal funding made up 25.8 percent of the funding, while in 2021 that percentage rose to 36.2 percent.
In 2019, federal funding made up only 7.1 percent of funding for operating expenses.
In Southwest Washington, C-TRAN’s percent of operating revenue to operating costs were as follows:
2021
- Fixed Route: 5.9 percent
- Demand Response: 1.7 percent
- Vanpool: 37.7 percent
2020
- Fixed Route: 7.3 percent
- Demand Response: 2.2 percent
- Vanpool: 28.3 percent
2019
- Fixed Route: 14.2 percent
- Demand Response: 3.5 percent
- Vanpool: 35.3 percent
This story was first published by The Center Square.
Also read:
- Clark College officially opens Advanced Manufacturing Center in RidgefieldClark College marked the official opening of its Advanced Manufacturing Center in Ridgefield, a new facility focused on training students for careers in advanced manufacturing.
- POLL: With updated estimates reaching as high as $17.7 billion, what should happen to the I-5 Bridge replacement project?A new poll asks readers how the I-5 Bridge replacement project should proceed amid higher cost estimates and questions about transparency within the Interstate Bridge Replacement Program.
- Letter: ‘Walz’s tough talk is a blatant attempt to deflect his complicity in the massive fraud in his state’Camas resident Anna Miller argues that a governor has no legal authority to deploy the National Guard to interfere with federal law enforcement and criticizes Minnesota Gov. Tim Walz’s public statements.
- VIDEO: Reykdal tells school districts to ‘abide by the law’ on trans athletesState Superintendent Chris Reykdal said Washington school districts must follow state law on transgender athletes as citizen initiatives and related Supreme Court cases move forward.
- County seeks community needs survey responses from residentsClark County Community Services is collecting survey responses from residents living on limited incomes to inform its required Community Needs Assessment and guide funding priorities for anti-poverty services.
- Opinion: Not a Good choiceLars Larson argues that personal choices led to a deadly confrontation with law enforcement during an ICE operation in Minneapolis.
- County Charter Review Commission to hold first two meetings in JanuaryThe Clark County Charter Review Commission will meet twice in January to begin reviewing the county’s charter and consider whether to recommend amendments for voter approval.